How to Migrate an On-Premises Oracle Database to OCI (Oracle Cloud Infrastructure)
- Oct 23, 2025
- 3 min read
Updated: Jan 29
Migrating an Oracle Database from an on-premises environment to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) is one of the most common modernization initiatives enterprises undertake today. Whether you’re looking for scalability, performance, or operational efficiency, OCI provides multiple deployment models — from Autonomous Database to Exadata Cloud Service — to match diverse workloads.
This guide walks you through a step-by-step approach to planning and executing a smooth Oracle database migration to OCI.
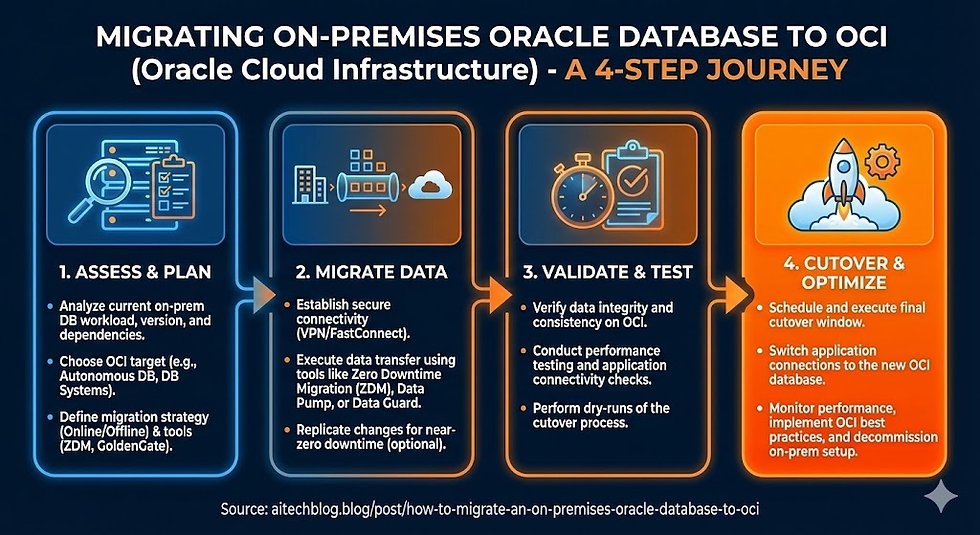
Step 1: Assess and Plan
Before starting the migration, perform a thorough assessment of your current environment.
1. Identify the Source Database
Determine the database version (11g, 12c, 19c).
Note the database size (in GB or TB).
Understand the architecture — whether it’s single instance, RAC, CDB/PDB, or Exadata-based.
2. Choose the Target Environment
Depending on your business needs, select the right OCI database service:
Autonomous Database: Ideal for modern workloads with minimal customization and self-management.
DB Systems (VM/BM): Best for environments requiring administrative control and OS-level access.
Exadata Cloud Service / Cloud@Customer: Suitable for large-scale, mission-critical databases that demand high performance and consolidation.
3. Check Compatibility
Verify endianness when migrating across platforms ( x86 vs. SPARC).
Ensure database features are compatible with the target version.
Convert non-CDB databases to PDB before moving to 21c or later versions.
Step 2: Choose the Right Migration Method
The method you select depends on database size, version, and acceptable downtime.
A. Low Downtime (Ideal for Banking and 24x7 Systems)
Oracle GoldenGate: Replicates data from on-premises to OCI in real time, enabling near-zero downtime during cutover. Recommended for critical production environments.
B. Medium Downtime
Oracle Data Guard: Create a standby database in OCI, sync it with the primary, and then perform a controlled switchover. Works effectively for Oracle 19c and similar environments.
C. Higher Downtime (Simple and Cost-Effective)
Oracle Data Pump (expdp/impdp): Export schemas or the full database, upload dump files to OCI Object Storage, and import into the target environment. Suitable for databases under 1 TB or non-critical applications.
D. Full Copy / Lift-and-Shift
RMAN Backup/Restore or Zero Downtime Migration (ZDM):Use RMAN to back up the source database, store backups in OCI Object Storage, and restore them in the cloud.Alternatively, Oracle’s ZDM automates this process, reducing manual effort and potential errors.
Step 3: Execute the Migration
Once the planning and method selection are complete, move on to execution.
1. Prepare the OCI Environment
Provision the target database service (Autonomous, VM, BM, or Exadata).
Configure networking components — VCNs, subnets, and security rules.
Set up OCI Object Storage for data transfer if needed.
2. Transfer Data
Use OCI CLI, Data Transfer Service, or FastConnect to move data dumps or backups efficiently.
For replication-based migrations (GoldenGate or Data Guard), ensure secure connectivity between on-prem and OCI.
3. Cutover
Validate the migrated data for accuracy and consistency.
Update application connection strings to point to the new OCI database.
Optionally, decommission the on-prem environment once testing is complete.
Step 4: Post-Migration Activities
After a successful cutover, perform post-migration checks and optimization:
Validate performance: Compare pre- and post-migration AWR reports.
Enable security: Activate Transparent Data Encryption (TDE), auditing, and access controls.
Set up monitoring: Use OCI Monitoring, Logging, and Alarms for real-time visibility.
Configure backups: Schedule automatic backups using OCI Database Backup Service.
Tune performance: Adjust parameters and indexes based on new workloads.
Final Thoughts
Migrating to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure is more than just a lift-and-shift — it’s an opportunity to modernize and optimize your database environment. With the right planning, migration tools, and post-migration governance, organizations can achieve better scalability, reliability, and total cost efficiency.
Whether you choose Autonomous Database for simplicity or Exadata Cloud Service for power, OCI offers the flexibility and resilience needed to run enterprise-grade Oracle workloads in the cloud.



Comments